What is a greenhouse ventilation?
Ventilation in greenhouses directly affects plant health and crop production. Temperature, humidity, and carbon dioxide (CO2) levels affect photosynthesis and the way plants grow and develop. A good ventilation system maintains proper environmental conditions and positively affects plant health and growth.
Without sufficient and proper ventilation, excess temperatures can cause poor plant growth, the need for more-frequent watering, and fans (if equipped) to run more often. All this adds up to higher costs and lower profits.
Types of ventilation
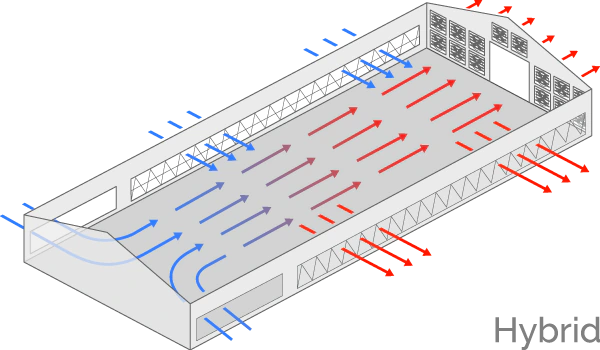
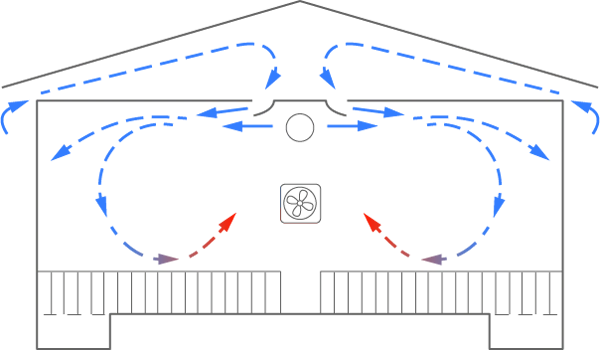
The ventilation system is a key component of the greenhouse design. The three most common systems are all-mechanical, mechanical/natural, and all-natural.
Mechanical ventilation
There are two categories of mechanical ventilation:
- A traditional system with air inlets in the ceiling and fans in the sidewall and pits;
- A three-season (fall, winter, and spring) system with traditional during the three seasons, but, adding tunnel ventilation during hot weather.
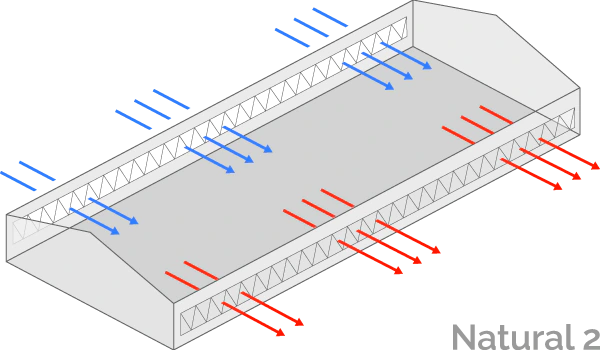
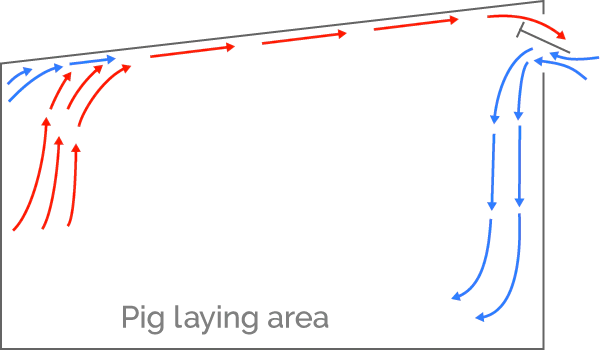
Natural ventilation
In natural ventilation, the barn is equipped with curtains in the sidewalls that are powered by motors called curtain machines or winches. These barns are sometimes referred to as “curtain-sided barns”. Natural mode is generally used during mild or moderate weather.
Curtain control uses an idle band. An idle band is a desired temperature range. When the temperature is within the idle band, the control maintains the curtain position. When the temperature rises above or drops below the idle band, the control adjusts the position of the curtains to allow more or less air into the building.
Negative, positive, and neutral pressure systems
- In negative pressure systems, fans exhaust the air out of the building and create negative pressure (a vacuum) that draws air into the building through inlets.
- In positive pressure systems, fans force air into the building and create positive pressure that forces air out through the inlets.
- In neutral pressure systems, fans exhaust air out of and force air into the building at the same time.